In today’s fast-paced world, the logistics and supply chain industry stands at the forefront of technological innovation, with geospatial analytics emerging as a powerhouse driving this transformation. Geospatial analytics has transcended from being a mere concept to a pivotal tool in reshaping the landscape of modern supply chain management. This groundbreaking technology is revolutionizing how companies approach logistics, from optimizing delivery routes to enhancing real-time decision-making.
The evolution of supply chain management has been remarkable. From the traditional methods reliant on manual processes and intuition-based decisions, the industry has moved towards embracing sophisticated technologies like geospatial analytics. This advancement is not just an upgrade; it’s a complete overhaul of the supply chain paradigm, introducing unprecedented levels of efficiency, accuracy, and reliability.
This article aims to delve deep into the realm of geospatial analytics in supply chain management. We will explore its transformative impact, unraveling how it redefines the logistics operations of the 21st century. From the nuts and bolts of the technology to its wide-ranging applications and benefits, we’re set to provide a comprehensive view of geospatial analytics as a cornerstone of contemporary supply chain solutions.
Understanding Geospatial Analytics in Supply Chain Management
Defining Geospatial Analytics
Geospatial analytics is an intricate blend of gathering, displaying, and manipulating imagery, GPS, satellite photography, and historical data. This technology provides insights based on geographical or spatial information, allowing businesses to visualize and analyze data with a geographic component. In the context of supply chain management, geospatial analytics becomes an invaluable tool, enabling companies to make more informed decisions based on the spatial and temporal context of their data.
Components of Geospatial Analytics
The backbone of geospatial analytics in supply chain management lies in its key components:
- GIS (Geographic Information Systems): This is the framework for gathering, managing, and analyzing spatial and geographic data. GIS technology provides a unique way of viewing and understanding data through maps and visualization, revealing hidden patterns, relationships, and trends.
- GPS (Global Positioning System): GPS technology is critical in tracking and monitoring the movement of goods in real-time. It offers precise location data, essential for route optimization, fleet management, and ensuring timely deliveries.
- Spatial Data Analysis: This involves the examination of both spatial and non-spatial data. It includes analyzing logistics networks, optimizing routes, site selection for warehouses, and assessing market demographics for strategic planning.
Role in Modern Supply Chains
The integration of geospatial analytics in supply chain management is a game-changer. It provides unparalleled supply chain visibility, allowing businesses to track and monitor their assets with exceptional precision. This enhanced visibility is not just about knowing the location of goods but understanding how various elements of the supply chain interact spatially and temporally. From optimizing delivery routes to minimizing transportation costs and improving customer satisfaction, geospatial analytics plays a pivotal role in making supply chains more efficient, responsive, and agile.
Integrating Geospatial Analytics into Supply Chain Operations
Assessing Supply Chain Needs
The first step in integrating geospatial analytics into supply chain operations is a thorough assessment of your current supply chain needs. Identify the specific areas where geospatial analytics can add the most value. This could involve areas like logistics route planning, warehouse location selection, or market analysis. Evaluate the existing data and systems for compatibility with geospatial tools. This assessment should also consider the geographical spread of your supply chain, as well as any unique logistical challenges posed by the locations you operate in.
Implementing Geospatial Tools
Once you’ve identified the areas for integration, the next step is selecting the right geospatial tools and technologies. This selection should align with your specific supply chain needs and goals. Consider tools that offer features like real-time tracking, GIS mapping, and spatial data analysis. The integration process should be gradual and systematic, starting with pilot projects to test the effectiveness of the tools before a full-scale implementation. It’s crucial to ensure that these tools are compatible with your existing IT infrastructure to facilitate seamless data flow and analysis.
Training and Skill Development
The success of geospatial analytics integration heavily relies on the skills and knowledge of your team. Invest in comprehensive training programs to equip your staff with the necessary skills for geospatial data interpretation and application. This training should cover not only the technical aspects of using the tools but also how to leverage the insights gained from geospatial analytics for strategic decision-making. Encourage a culture of continuous learning and innovation to keep your team updated with the latest geospatial technologies and practices.
Accelerating Growth in the Geospatial Analytics Market
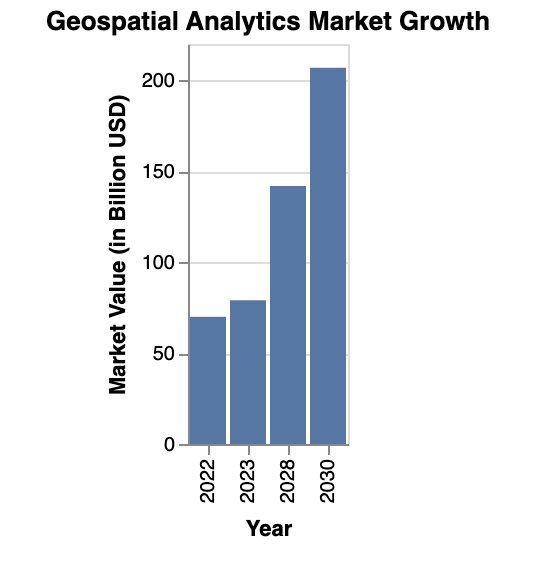
The global geospatial analytics market is witnessing a remarkable surge, as depicted in the recent bar chart analysis. This section delves into the implications and drivers of this growth, particularly within the context of supply chain management.
Unprecedented Market Expansion
In 2022, the market value of geospatial analytics stood at USD 69.96 billion. This figure is significant, considering the niche nature of this technology. However, the forecast for the coming years is even more striking. By 2023, the market is expected to grow to approximately USD 79.06 billion, showcasing a robust year-on-year growth. The real leap, however, is projected for 2030, where the market value is estimated to reach a staggering USD 206.93 billion.
Driving Factors Behind the Growth
Several key factors contribute to this exponential growth. Firstly, the increasing urbanization and technological advancements across the globe play a pivotal role. Businesses are investing more in IT solutions, and geospatial analytics is a prime example of this trend. Secondly, the growing application of geospatial analytics in various sectors, especially in supply chain management, has expanded its market reach.
Impact on Supply Chain Management
In the realm of supply chain management, geospatial analytics is no longer a futuristic concept but a current necessity. It allows for enhanced route optimization, risk management, and strategic planning. For instance, real-time tracking and predictive analytics enabled by geospatial tools help companies to preemptively address potential supply chain disruptions. This not only streamlines operations but also significantly reduces costs and improves customer satisfaction.
Looking Forward
As the geospatial analytics market continues to grow, its integration into supply chain management becomes increasingly vital. Companies that leverage this technology will gain a competitive edge through improved efficiency and decision-making capabilities. The future of supply chain management is inextricably linked with the advancements in geospatial analytics, making it an indispensable tool for businesses aiming for resilience and growth in a rapidly evolving global market.
Key Benefits and Applications of Geospatial Analytics in Supply Chains
Route Optimization and Transportation Management
One of the most significant benefits of geospatial analytics in supply chains is route optimization. By analyzing spatial data, companies can plan the most efficient routes for transportation, reducing travel time and fuel costs. Real-time tracking enabled by geospatial tools enhances the visibility of logistics operations, allowing for timely interventions in case of delays or disruptions.
Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Geospatial analytics is instrumental in identifying potential risks in the supply chain, such as natural disasters, political unrest, or transportation bottlenecks. By analyzing geographic and spatial data, companies can develop robust contingency plans to mitigate these risks. This proactive approach to risk management ensures greater resilience and reliability in supply chain operations.
Market Analysis and Expansion Strategies
Geospatial analytics provides valuable insights for market analysis and expansion strategies. By analyzing demographic and geographic data, companies can identify new market opportunities and plan strategic expansions. This includes determining optimal locations for new warehouses or retail outlets based on proximity to target markets and supply chain infrastructure.
Geospatial analytics offers a multitude of benefits and applications that can significantly enhance the efficiency, resilience, and strategic capabilities of modern supply chain operations. By effectively integrating these tools and leveraging their insights, companies can not only optimize their current operations but also strategically plan for future growth and success.
Future Trends in Geospatial Analytics for Supply Chains
Emerging Trends and Technological Advancements
The future of geospatial analytics in supply chain management is marked by exciting trends and technological advancements. The integration of AI and machine learning with geospatial tools is set to offer more precise predictive analytics and real-time decision-making capabilities. We are seeing the emergence of more sophisticated GIS software that can handle larger datasets, offering deeper insights into supply chain dynamics. The use of drone technology for aerial mapping and real-time tracking of assets is another trend gaining momentum. Additionally, the increasing adoption of IoT devices will enhance the data collection process, providing more granular, location-based insights.
Overcoming Challenges and Limitations
Implementing geospatial analytics in supply chains comes with its set of challenges. Data privacy and security remain primary concerns, especially when handling sensitive geographic information. The complexity and cost of implementing advanced geospatial systems can also be a barrier for some organizations. Overcoming these challenges requires a balanced approach, focusing on robust cybersecurity measures, investing in scalable solutions, and training employees to handle geospatial data effectively.
Strategic Importance in Global Supply Chain Networks
Geospatial analytics plays a strategic role in enhancing the resilience and competitiveness of global supply chain networks. By providing comprehensive spatial insights, it aids in mitigating risks associated with global logistics, such as political instability, natural disasters, and market volatility. Geospatial analytics empowers businesses to make informed decisions about route planning, warehouse locations, and market expansions, thereby enhancing operational efficiency and strategic positioning in the global market.
FAQs on Geospatial Analytics in Supply Chain Management
How does geospatial analytics improve supply chain efficiency?
Geospatial analytics enhances efficiency by optimizing routes, improving asset tracking, and providing spatial data for better decision-making.
What are the key challenges in implementing geospatial analytics in supply chains?
Key challenges include the complexity of integration, data security concerns, and the need for specialized skills to interpret geospatial data.
Can small businesses benefit from geospatial analytics?
Yes, even small businesses can benefit by using basic geospatial tools for local market analysis, route optimization, and competitive positioning.
Expert Insights and Practical Tips
Expert Insight: Start small with geospatial analytics. Begin by integrating basic GIS tools and gradually expand as you understand its impact on your operations.
Practical Tip: Regularly update your geospatial data and train your team on the latest geospatial technologies and trends to stay ahead in the competitive supply chain landscape.
In conclusion, geospatial analytics is rapidly transforming the landscape of supply chain management. From enhancing operational efficiency to strategic market analysis, its applications are diverse and impactful. As we navigate the complexities of the modern supply chain, the integration of geospatial analytics emerges as a crucial component for success. It not only provides a competitive edge but also drives innovation and strategic decision-making in supply chain management. The future of efficient, resilient, and competitive supply chains is inextricably linked with the advancements in geospatial analytics, making it an indispensable tool for businesses looking to thrive in the global market.