In the realm of supply chain management, a revolutionary wave is reshaping the very foundations of production and distribution – and it’s known as 3D printing technology. This groundbreaking advancement stands at the forefront of industrial innovation, heralding a new era where the constraints of traditional manufacturing and supply chain logistics are being dismantled. 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is not just a tool; it’s a paradigm shift offering unprecedented flexibility and efficiency in creating and delivering products.
As we venture into this new era, 3D printing is redefining the dynamics of production and distribution. It empowers businesses to move from mass production to customization, from centralized manufacturing to localized production, and from inventory-based models to on-demand manufacturing. This intersection of innovation and efficiency is not just enhancing supply chain operations; it’s creating new possibilities and avenues for businesses to explore and capitalize on.
This article aims to delve deep into the transformative role of 3D printing in supply chain solutions. We will explore the technology’s fundamentals, trace its evolutionary journey, and examine its growing influence in modern supply chains. From dissecting the benefits to addressing the challenges, this piece seeks to provide a comprehensive understanding of how 3D printing is reshaping supply chain management and what the future holds for this exciting technology.
Understanding 3D Printing in Supply Chain Management
Basics of 3D Printing Technology
3D printing, at its core, is a process that creates objects by adding material layer by layer, based on digital models. This technology has several key components, including 3D printers, specialized software for design and printer control, and various materials such as plastics, metals, and composites. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods that involve cutting away material to shape an object, 3D printing builds the object directly from the raw material, reducing waste and allowing for complex designs that would be impossible or prohibitively expensive with conventional techniques.
Evolution of 3D Printing
The journey of 3D printing from a niche prototyping tool to a mainstream manufacturing technology is a testament to its transformative potential. Initially developed in the 1980s for rapid prototyping, 3D printing technology has seen significant advancements in speed, precision, material diversity, and scalability. Its adoption across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and consumer goods, signifies a growing recognition of its benefits in reducing lead times, lowering costs, and enhancing product customization.
3D Printing’s Role in Modern Supply Chains
In the context of modern supply chains, 3D printing is increasingly becoming a strategic tool. It enables businesses to reduce inventory costs by producing goods on demand, close to the point of need, thus minimizing the need for extensive warehousing and logistics. This shift to on-demand production also allows for greater responsiveness to market changes and customer preferences. Moreover, 3D printing facilitates local production, reducing the dependence on complex, global supply chains and mitigating risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
The integration of 3D printing into supply chain strategies is not just a trend; it’s a shift towards more agile, cost-effective, and customer-centric operations. As we continue to explore this technology’s capabilities and applications, its role in shaping efficient and resilient supply chains becomes increasingly evident.
Integrating 3D Printing into Your Supply Chain
Assessing Suitability for 3D Printing
Before integrating 3D printing into your supply chain, it’s crucial to evaluate if this technology aligns with your business objectives and operational needs. Begin by analyzing your product portfolio to identify items that could be efficiently produced using 3D printing. Consider factors like the complexity of designs, material requirements, and production volumes. Assess the potential for reducing inventory costs and improving production flexibility. Also, evaluate your current supply chain challenges – could 3D printing help in addressing issues like supply chain disruptions, long lead times, or high warehousing costs? This initial assessment is vital in determining the feasibility and potential benefits of 3D printing for your business.
Implementation Strategy
Once you’ve identified the potential of 3D printing for your business, developing a structured implementation strategy is key.
- Equipment Selection: Choose the right 3D printers based on your product requirements, such as material compatibility and print capacity.
- Staff Training: Ensure your team is equipped with the necessary skills. This might involve training existing staff or hiring new talent with expertise in 3D printing technologies.
- Workflow Adjustments: Integrate 3D printing into your existing production processes. This may require redefining workflows, setting up new production lines, or establishing protocols for quality control and testing.
- Supplier Collaboration: If outsourcing 3D printing, establish partnerships with reliable 3D printing service providers. For in-house operations, build relationships with material suppliers.
- Testing and Scaling: Start with a pilot project to test the effectiveness of 3D printing. Once validated, scale the operation to other areas of your business where 3D printing could be beneficial.
Optimizing 3D Printing for Supply Chain Efficiency
To maximize the benefits of 3D printing in your supply chain, focus on areas where it can add the most value. Use 3D printing for producing complex, customized components that are otherwise expensive or time-consuming to manufacture. Leverage its capability for rapid prototyping to accelerate product development cycles. Continuously monitor the performance and output of your 3D printing operations and make adjustments to ensure optimal efficiency and quality. Additionally, keep abreast of the latest advancements in 3D printing technology to continually enhance your supply chain capabilities.
3D Printing: A Catalyst for Supply Chain Transformation
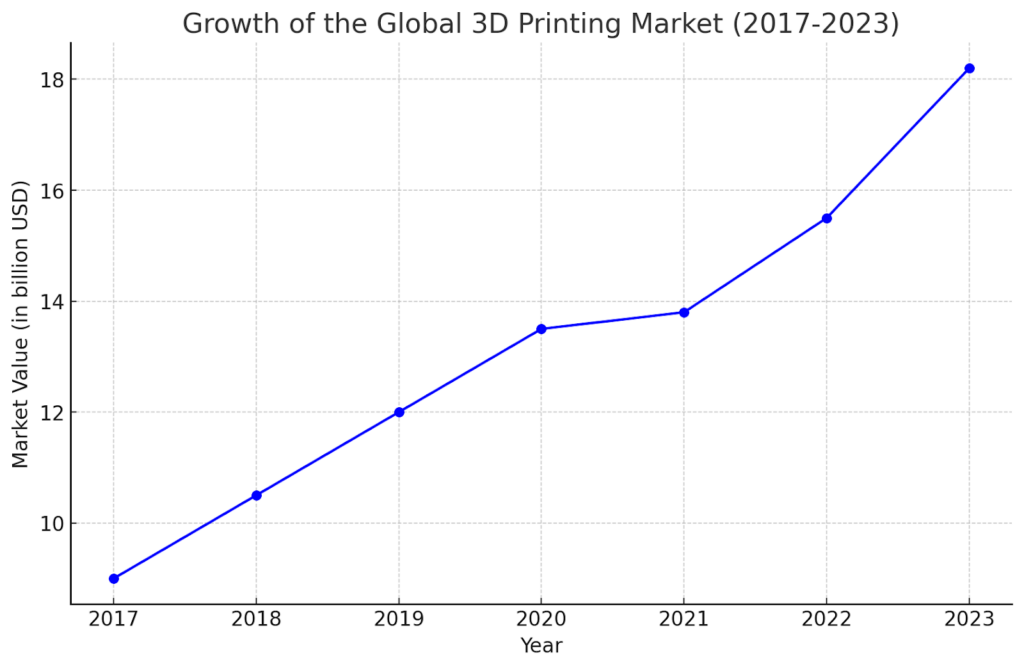
The line graph vividly illustrates the remarkable growth trajectory of the global 3D printing market from 2017 to 2023. Beginning at a market value of around $9 billion in 2017, the industry experienced a consistent and significant upsurge, reaching an estimated $18.2 billion by 2023. This exponential growth reflects the increasing embrace of 3D printing technologies across various sectors, particularly in supply chain management.
The graph underscores a pivotal shift in manufacturing and logistics paradigms. With 3D printing at the helm, businesses are transitioning from traditional, inventory-heavy models to more agile, on-demand production approaches. This evolution is not just about technological advancement; it represents a strategic reorientation towards localized production, minimizing lead times, and enhancing responsiveness to market demands.
As we delve deeper into the implications of this growth, it becomes evident that 3D printing is not merely an innovative manufacturing tool. It is a transformative force reshaping the very fabric of supply chain operations. The ability to produce goods closer to the point of need, coupled with the technology’s inherent flexibility, is paving the way for more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable supply chain solutions.
Looking ahead, the ongoing integration of 3D printing into supply chain strategies heralds a future where personalized production, reduced environmental impact, and supply chain resilience are not just aspirations but tangible realities. The continued development and adoption of this technology will likely unlock further potential, challenging traditional manufacturing norms and opening new avenues for business innovation and growth.
Top 10 Impacts of 3D Printing on Supply Chain Management
- Customization and Personalization: 3D printing allows for high levels of customization, enabling businesses to tailor products to specific customer preferences without significant production adjustments.
- Reducing Lead Times and Inventory Costs: By enabling on-demand production, 3D printing significantly cuts down lead times and reduces the need for large inventory stocks, freeing up capital and space.
- Sustainability: 3D printing minimizes waste by using only the necessary material for each product, contributing to more sustainable manufacturing processes.
- On-Demand Production: It allows for the production of items as and when needed, reducing overproduction and associated costs.
- Risk Reduction: With localized production, 3D printing reduces dependence on complex supply chains, mitigating risks such as delays and disruptions.
- Quality Improvement: Advanced 3D printing technologies can produce high-quality products with precision, improving overall product quality.
- Logistical Efficiency: Localized production using 3D printing can simplify logistics and distribution, reducing transportation costs and times.
- Cost Reduction: It can lower production costs by reducing material waste, decreasing storage needs, and simplifying the manufacturing process.
- Innovation in Product Design: 3D printing enables complex and innovative product designs that may be impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.
- Enhanced Collaboration: The flexibility of 3D printing encourages collaboration between designers, engineers, and manufacturers, fostering innovation and creativity.
Integrating 3D printing into supply chain operations offers significant benefits, from enhancing product customization to improving efficiency and sustainability. By understanding and strategically implementing this technology, businesses can revolutionize their supply chain solutions and gain a competitive edge in the market.
The Future of Supply Chains with 3D Printing
Predicting Trends in 3D Printing and Supply Chain Management
The future of supply chains is being redefined by the advancements in 3D printing technology. We are likely to witness a significant shift towards localized production, as 3D printing allows businesses to manufacture products closer to the point of consumption, reducing the need for extensive logistics networks. Another emerging trend is the increased use of 3D printing for producing spare parts on demand, which can drastically reduce downtime in various industries. Additionally, the continuous development in printing materials and techniques will expand the range of products that can be produced, potentially disrupting traditional manufacturing sectors.
Challenges and Opportunities Ahead
While 3D printing presents numerous opportunities for supply chain optimization, it also brings challenges that need to be addressed. One major challenge is the initial investment in 3D printing technology and the required expertise. There’s also the task of integrating this technology into existing supply chain processes seamlessly. However, these challenges are outweighed by the opportunities, which include greater flexibility in production, reduced lead times, and the potential for mass customization of products. Businesses that successfully navigate these challenges will be well-positioned to capitalize on the benefits of 3D printing.
3D Printing as a Catalyst for Sustainable Practices
3D printing holds great promise for promoting sustainability in supply chain solutions. This technology reduces material wastage through its additive manufacturing process, supports the production of lighter and stronger parts, and minimizes the carbon footprint associated with transportation in traditional manufacturing and supply chain models. By enabling more sustainable production processes, 3D printing is not just an innovative solution but also a catalyst for environmentally friendly practices in supply chain management.
FAQs on 3D Printing in Supply Chain Solutions
Can 3D printing be integrated into any type of supply chain?
3D printing is versatile but may not be suitable for all types of supply chains. It’s most beneficial in industries where customization, complex designs, and on-demand production are valuable.
What are the cost implications of adopting 3D printing in supply chains?
The initial investment in 3D printing can be significant, but it can reduce long-term costs by lowering inventory and warehousing expenses, and minimizing waste.
How does 3D printing impact lead times in supply chain management?
3D printing significantly reduces lead times, allowing businesses to produce and deliver products faster, responding more promptly to customer demands.
Expert Insights and Practical Advice
Expert Insight: To effectively integrate 3D printing, businesses should start with pilot projects focusing on specific parts of their supply chain where the technology can have the most immediate impact.
Practical Advice: Stay informed about the latest developments in 3D printing materials and technologies to continually assess how they can benefit your specific supply chain needs.
In conclusion, 3D printing is poised to play a pivotal role in the evolution of supply chain management. By enabling on-demand production, reducing lead times, and promoting sustainability, 3D printing technology offers a path to more efficient, innovative, and environmentally friendly supply chain solutions. As we embrace these advancements, the future of supply chain management looks towards a landscape where agility, customization, and sustainability are not just aspirations but achievable realities. The ongoing integration of 3D printing into supply chains is not just a technological shift, but a strategic move towards reshaping how businesses produce, distribute, and innovate in the global marketplace.