Logistics is the lifeline of modern commerce, ensuring that products move efficiently from manufacturers to consumers. The logistics cycle encompasses various critical stages, each playing a pivotal role in the seamless movement of goods. This article explores the logistics cycle in detail, highlighting the importance of each step and offering insights into how businesses can optimize these processes for improved efficiency and customer satisfaction. By understanding each stage’s intricacies, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
Procurement
The logistics cycle begins with procurement, the process of sourcing and acquiring the raw materials and components needed for production. This step is crucial as it sets the foundation for the entire supply chain. Effective procurement involves selecting reliable suppliers, negotiating favorable terms, and ensuring that materials are delivered on time and meet quality standards. Strategic sourcing can significantly reduce costs and mitigate risks associated with supply disruptions. For example, companies often use strategic partnerships and long-term contracts to ensure a steady supply of critical materials. In addition to cost savings, effective procurement strategies can enhance product quality and reduce lead times, providing a competitive edge in the market.
Transportation
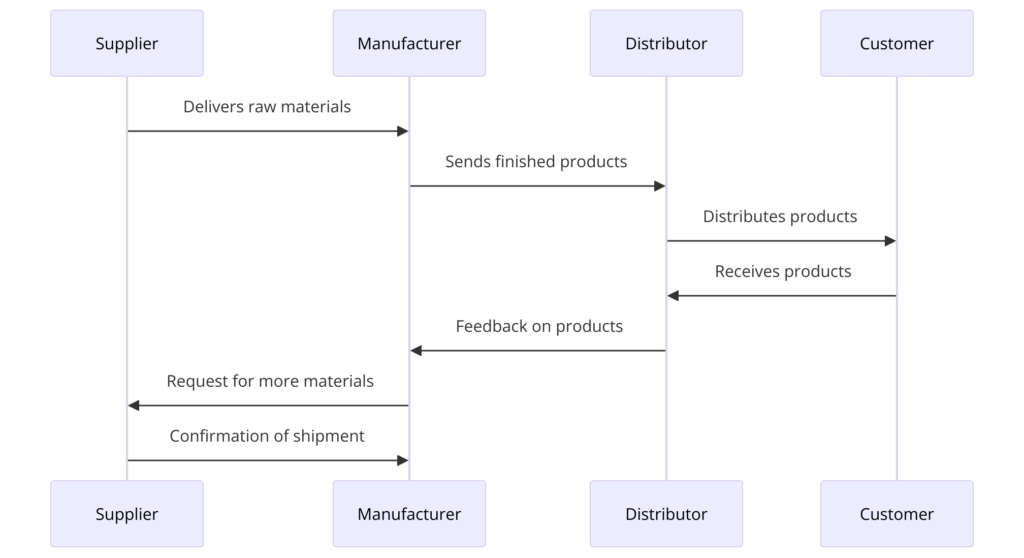
Transportation is the next critical step in the logistics cycle, involving the movement of goods from suppliers to manufacturers, between manufacturing sites, and finally to distribution centers and customers. Efficient transportation management ensures timely delivery, reduces costs, and minimizes environmental impact. Companies use various modes of transport, including road, rail, air, and sea, depending on the nature of the goods and the delivery requirements. Advanced transportation management systems (TMS) help optimize routes, track shipments in real-time, and manage transportation costs effectively. For instance, logistics companies like FedEx and UPS rely heavily on sophisticated TMS to enhance their delivery services. Additionally, innovations like autonomous vehicles and drones are gradually being integrated to further streamline transportation logistics.
Warehousing
Warehousing is essential for storing goods at various stages of the logistics cycle. It involves receiving, storing, and managing inventory until it is needed for production or delivery. Effective warehouse management ensures that goods are stored safely and can be retrieved quickly when needed. Technologies such as automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) and warehouse management systems (WMS) improve efficiency and accuracy in warehouse operations. These systems help manage inventory levels, reduce storage costs, and improve order fulfillment times. For example, Amazon’s fulfillment centers use a combination of robotics and human labor to optimize warehouse operations. Efficient warehousing not only ensures timely availability of goods but also plays a crucial role in maintaining product quality and reducing loss through damage or obsolescence.
Inventory Management
Inventory management involves overseeing the flow of goods from manufacturers to warehouses and ultimately to customers. This step ensures that there is enough stock to meet customer demand without overstocking, which ties up capital and increases storage costs. Techniques such as just-in-time (JIT) inventory, economic order quantity (EOQ), and ABC analysis help maintain optimal inventory levels. Effective inventory management improves cash flow, reduces holding costs, and ensures product availability, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction. Advanced inventory management systems provide real-time data on inventory levels, helping businesses make informed decisions about stock replenishment. Companies like Walmart and Zara use sophisticated inventory management techniques to respond quickly to market demands and maintain optimal stock levels.
Order Processing
Order processing is the process of receiving and fulfilling customer orders. It includes order entry, picking, packing, and shipping. Efficient order processing ensures that customers receive the correct products in a timely manner. Order management systems (OMS) streamline the process, reduce errors, and improve delivery times. Automation in order processing can significantly enhance efficiency, as seen in companies like Amazon and Walmart, which use automated systems to handle large volumes of orders quickly and accurately. This step is crucial for maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction and loyalty. Efficient order processing systems also provide businesses with valuable data on order trends and customer preferences, helping them tailor their offerings and improve service levels.
Distribution
Distribution involves delivering the final product to the customer. This step includes managing distribution centers, selecting carriers, and coordinating delivery schedules. Efficient distribution ensures that products reach customers on time and in good condition. Last-mile delivery, the final leg of the delivery process, is particularly challenging and critical for customer satisfaction. Technologies such as GPS tracking and delivery management software help optimize delivery routes and provide real-time updates to customers. Companies like Amazon and DHL have invested heavily in optimizing their last-mile delivery operations to meet the growing demands of e-commerce. Additionally, sustainable distribution practices, such as using electric vehicles for deliveries, are being adopted to reduce environmental impact and meet regulatory standards.
Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics refers to the process of returning products from customers back to the retailer or manufacturer. This can include returns, recycling, refurbishing, and disposal of products. Efficient reverse logistics is essential for managing returns cost-effectively, minimizing waste, and ensuring customer satisfaction. It also plays a critical role in sustainability by facilitating the reuse and recycling of materials, reducing the environmental impact of products. Companies like Apple and HP have robust reverse logistics systems to handle product returns and recycling efficiently. Effective reverse logistics can also enhance brand reputation by demonstrating a commitment to sustainability and customer service.
In Conclusion
The logistics cycle is a complex but essential process that ensures the smooth movement of goods from suppliers to customers. Each step, from procurement to reverse logistics, plays a crucial role in maintaining efficiency and customer satisfaction. By understanding and optimizing each stage of the logistics cycle, businesses can reduce costs, improve service levels, and gain a competitive edge. For further insights and strategies, exploring resources from industry experts and staying updated with the latest technological advancements can provide valuable guidance in navigating the logistics landscape. Implementing these strategies effectively can transform logistics operations, driving business success and enhancing customer experiences.