Logistics is a crucial field that involves managing the movement and coordination of goods, services, and information across various channels, from raw materials to finished products. This management includes several aspects such as transportation, warehousing, inventory management, and distribution. Each of these areas plays a significant role in ensuring the efficient delivery of goods to customers. Additionally, logistics professionals must manage supply chain networks, ensuring smooth collaboration between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors to maintain an uninterrupted flow of goods.
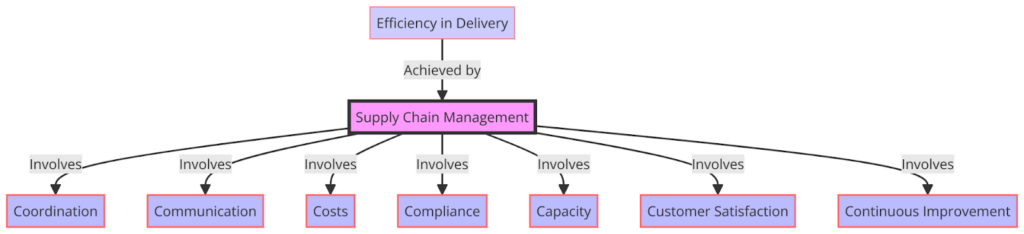
To understand the intricacies of logistics, it can be broken down into seven essential components or “C’s,” each encompassing key aspects of supply chain management. These include Coordination, Communication, Costs, Compliance, Capacity, Customer Satisfaction, and Continuous Improvement. Understanding these components provides a comprehensive view of modern logistics operations and their challenges.
This article delves into these seven C’s, exploring each component’s role and importance in managing modern logistics operations. We’ll cover how these elements contribute to the overall efficiency of supply chain management and provide insights for professionals and students considering a career in logistics.
1. Coordination
Scope
Coordination involves managing the flow of goods and services across various stages of the supply chain, ensuring seamless interactions between stakeholders. This includes managing the entire journey from suppliers and manufacturers to distributors and customers. The process covers several logistical aspects, including transportation, warehousing, and distribution, to achieve cost-effective and timely deliveries. Proper coordination also includes balancing inventory levels, meeting customer demands, and avoiding overstocking or understocking situations. Additionally, coordination ensures smooth collaboration between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors, maintaining the flow of goods across the supply chain.
Challenges
Effective coordination requires balancing costs, speed, and quality, necessitating strong communication and collaboration across the supply chain. Misalignment or inefficiencies at any stage can lead to disruptions, delays, or increased costs, making coordination a crucial element in logistics management. For instance, communication breakdowns between suppliers and manufacturers can lead to delayed deliveries or production stoppages. Coordination must also adapt to market changes, such as seasonal demand fluctuations or global economic shifts, which may require adjusting supply chain strategies. Effective coordination requires addressing these challenges while maintaining a balanced, efficient supply chain.
2. Communication
Importance
Clear communication between supply chain stakeholders is essential for efficient operations. This includes internal communication within companies, ensuring alignment between departments, and external communication with suppliers and customers, ensuring smooth transactions. Communication plays a critical role in addressing potential issues, such as delivery delays, quality concerns, or unexpected demand changes. By maintaining open lines of communication, companies can resolve these issues promptly and avoid further disruptions.
Technological Integration
Technological tools, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and communication platforms, facilitate real-time information sharing, enhancing operational efficiency. ERP systems integrate various functions, from procurement to sales, allowing stakeholders to monitor progress and coordinate effectively. Communication platforms enable seamless interaction, allowing teams to collaborate and address issues quickly. This integration of technology not only improves communication efficiency but also contributes to data-driven decision-making and streamlined operations.
3. Costs
Cost Management
Controlling costs is a crucial aspect of logistics management, requiring careful analysis and optimization across various areas. This includes monitoring and managing expenses related to transportation, warehousing, and inventory management. For example, transportation costs can be reduced by optimizing delivery routes, consolidating shipments, and negotiating contracts with carriers. Warehousing costs can be managed by improving storage efficiency, reducing handling times, and utilizing technology to track inventory and minimize excess stock. Inventory management costs can be minimized by balancing supply and demand, reducing overstocking, and implementing just-in-time (JIT) practices to prevent holding costs.
Strategies
Various strategies can help reduce logistics costs and improve overall efficiency. Bulk purchasing allows companies to negotiate discounts with suppliers, reducing the cost per unit. Outsourcing certain logistics functions, such as transportation or warehousing, can also lead to cost savings, allowing companies to focus on their core competencies. Route optimization, through technological solutions like GPS and data analytics, can streamline transportation processes, reducing fuel costs and delivery times. Additionally, utilizing technology, such as ERP systems, can provide a comprehensive view of costs across the supply chain, enabling companies to identify and implement cost-saving measures.
4. Compliance
Regulatory Requirements
Logistics operations must comply with various regulations, including import/export laws, environmental standards, and industry-specific guidelines. Import/export laws can impact the movement of goods across borders, necessitating compliance with customs regulations and trade agreements. Environmental standards may require companies to reduce emissions, minimize waste, and implement sustainable practices. Industry-specific guidelines, such as food safety standards or pharmaceutical regulations, can also dictate logistics processes, necessitating strict adherence to avoid legal issues.
Adapting to Changes
Staying current with regulatory changes is essential for maintaining smooth operations. This includes monitoring changes to import/export laws, environmental regulations, and industry guidelines, ensuring compliance to avoid disruptions. For instance, companies may need to adapt to new tariffs or trade agreements that impact global supply chains. Similarly, changes to environmental standards may necessitate adjustments to transportation methods or packaging materials. Adapting to these changes ensures logistics operations remain compliant, minimizing legal risks and maintaining efficient processes.
5. Capacity
Resource Allocation
Capacity management involves balancing available resources with operational demands, ensuring efficient logistics operations. This includes managing transportation, warehousing, and labor resources to meet supply chain needs. For example, companies may need to allocate additional transportation resources during peak seasons to meet increased demand. Similarly, warehousing capacity must be balanced with inventory levels to avoid overstocking or understocking situations. Proper resource allocation ensures smooth supply chain operations, minimizing delays and maintaining customer satisfaction.
Scalability
Adjusting capacity to match market fluctuations and seasonal demands is essential for efficient logistics operations. This involves scaling transportation, warehousing, and labor resources up or down as needed. For instance, companies may increase transportation resources during holiday seasons to handle increased shipping volumes. They may also scale back labor resources during off-peak periods to reduce costs. By effectively managing scalability, companies can maintain efficient logistics operations, meet customer demands, and achieve long-term success.
6. Customer Satisfaction
Meeting Expectations
Logistics operations must align with customer expectations, including timely delivery, accurate tracking, and responsive service. In modern supply chains, customers expect accurate and timely information on their orders, making tracking and delivery crucial. SCM professionals must ensure that products are delivered on time and without damage, maintaining a seamless experience for customers. This includes optimizing shipping routes, managing distribution centers efficiently, and addressing potential disruptions promptly. Customer feedback can also guide improvements, helping logistics operations align with evolving expectations.
Quality Assurance
Ensuring product quality and minimizing errors throughout the supply chain are essential for maintaining customer trust and loyalty. This requires careful quality checks at every stage, from manufacturing to packaging and shipping. Additionally, SCM professionals must implement processes that prevent defects, ensuring that products meet customer standards upon delivery. Quality assurance helps to reduce returns and complaints, maintaining positive relationships with customers.
7. Continuous Improvement
Ongoing Optimization
Regularly reviewing and refining logistics processes enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and improves overall performance. This includes evaluating current practices, identifying inefficiencies, and implementing changes to streamline operations. Continuous improvement also involves benchmarking against industry standards, ensuring logistics processes remain competitive. Implementing regular reviews and performance metrics can help track progress and guide further enhancements.
Technological Advancements
Integrating new technologies, such as AI and IoT, into logistics operations can drive continuous improvement. AI algorithms can optimize supply chain processes, from demand forecasting to inventory management. The Internet of Things (IoT) allows real-time tracking of goods, improving visibility and reducing delays. Blockchain technology can also provide transparency and security for supply chain transactions, reducing fraud and ensuring authenticity. These advancements contribute to streamlined operations and data-driven decision-making, supporting continuous improvement.
In Conclusion
The seven C’s of logistics—Coordination, Communication, Costs, Compliance, Capacity, Customer Satisfaction, and Continuous Improvement—are essential for managing modern supply chains. These components provide a comprehensive approach to logistics, balancing operational efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and sustainable practices. Coordination ensures smooth interactions between supply chain stages, while communication and compliance maintain alignment and regulatory adherence. Managing costs, resources, and capacity enhances logistics efficiency, and continuous improvement strategies drive operational refinement. Mastering these aspects contributes to efficient logistics, sustainable growth, and competitive supply chain operations. This holistic approach enables companies to navigate complex logistics landscapes, meeting customer expectations and achieving long-term success.