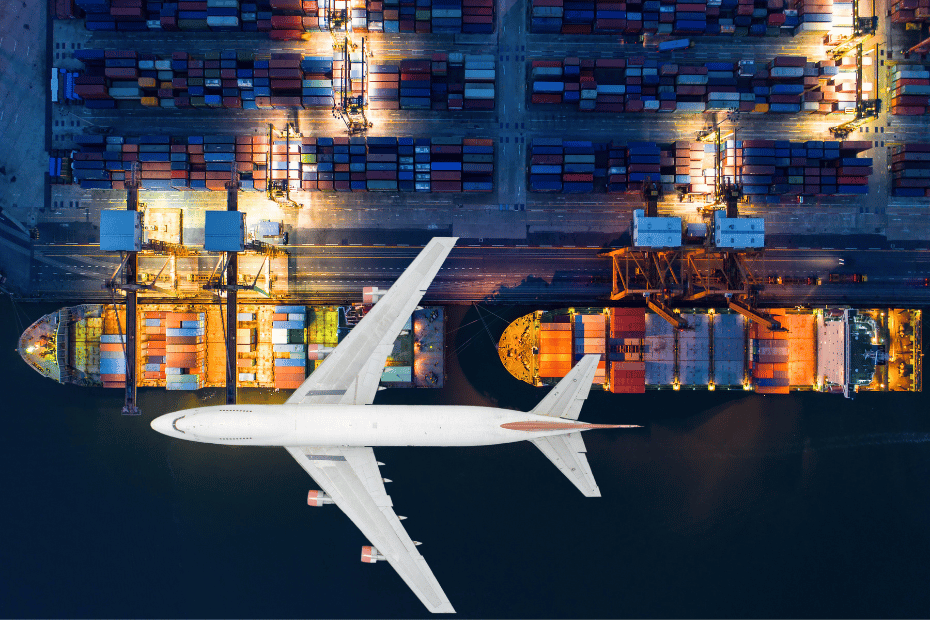
Logistics is a crucial field in supply chain management that involves managing the flow of goods, services, and information. This management ensures seamless coordination from origin to end-user, encompassing various functions such as transportation, warehousing, and inventory management. Logistics professionals must oversee these functions, ensuring that goods reach their intended destinations efficiently and effectively. This includes managing multiple aspects, such as supplier relations, distribution channels, and customer service, contributing to the overall success of modern logistics operations.
The complexity of logistics can be distilled into three key functions transportation, warehousing, and inventory management. Transportation ensures the movement of goods across the supply chain, covering various modes such as trucking, shipping, rail, and air freight. Warehousing provides storage solutions for goods at various stages, allowing companies to manage inventory levels and balance supply and demand. Inventory management focuses on balancing supply and demand, preventing overstocking or understocking situations, and ensuring timely restocking. These functions form the backbone of logistics, maintaining efficient and sustainable operations across modern supply chains.
This article delves into these three key functions, providing insights into each aspect’s role and importance in managing modern logistics operations. We explore how transportation, warehousing, and inventory management contribute to seamless supply chains and how they can be optimized for efficiency.
1. Transportation
Scope
Transportation covers the movement of goods from suppliers to manufacturers, distributors, and end-users, ensuring a seamless flow throughout the supply chain. This function includes various modes of transportation, such as trucking, shipping, rail, and air freight. Each mode offers unique advantages, allowing for diverse supply chain strategies that suit different industries and market needs. For instance, trucking provides flexibility and accessibility for short to medium distances, while shipping is cost-effective for large volumes and long distances. Rail offers stability and consistency, making it ideal for heavy goods over long distances. Air freight provides rapid delivery, particularly useful for time-sensitive or high-value items.
Optimization
Optimizing transportation efficiency and reducing costs requires careful route planning, shipment consolidation, and real-time tracking. Route planning software can analyze various factors such as distance, traffic, and weather conditions to determine the most efficient delivery routes. Shipment consolidation allows for combining smaller shipments into larger ones, reducing transportation costs and improving efficiency. Real-time tracking provides visibility into the progress of goods across the supply chain, enabling companies to monitor shipments, address potential delays promptly, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Furthermore, integrating technology like GPS and RFID can streamline tracking and routing processes, enhancing overall efficiency. Data analytics can also play a role in optimizing transportation, providing insights into shipping patterns, costs, and potential improvements.
2. Warehousing
Storage
Warehousing provides storage solutions for goods at various stages of the supply chain, including raw materials, in-process goods, and finished products. These storage solutions allow companies to manage inventory levels, balancing supply and demand. Warehousing can also reduce transportation costs by centralizing distribution points, minimizing travel distances for goods to reach end-users.
Different types of warehousing options exist, including dedicated warehouses, third-party logistics (3PL) providers, and distribution centers. Dedicated warehouses provide exclusive storage for a single company’s goods, offering control over inventory and management. 3PL providers offer outsourced warehousing solutions, allowing companies to focus on their core competencies while delegating storage management. Distribution centers serve as hubs for goods to be sorted, processed, and shipped to various destinations.
Management
Efficient warehousing management includes inventory tracking, order fulfillment, and minimizing storage costs. Inventory tracking technologies, such as barcode scanning and RFID, help monitor inventory levels, reducing stock discrepancies and ensuring timely restocking. Order fulfillment processes can be streamlined by optimizing picking, packing, and shipping workflows, minimizing handling times and improving efficiency.
Minimizing storage costs requires managing warehouse space effectively, avoiding overstocking or underutilization. This includes implementing strategies such as cross-docking, which moves goods directly from incoming to outgoing shipments, reducing storage time. Additionally, implementing warehouse management systems (WMS) can help automate storage processes, providing real-time visibility into inventory levels and improving overall efficiency.
3. Inventory Management
Balance
Inventory management balances supply and demand, preventing overstocking or understocking situations. This includes monitoring inventory levels, ensuring timely restocking, and implementing just-in-time (JIT) practices to minimize holding costs. Balancing supply and demand requires analyzing market trends, demand patterns, and lead times, allowing companies to forecast inventory needs accurately.
Additionally, inventory management involves managing reorder points and safety stock levels, ensuring sufficient inventory is available to meet customer demands while minimizing excess stock. Strategies such as JIT can help reduce inventory holding costs by receiving goods as needed, avoiding unnecessary storage expenses.
Technology
Technologies like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and data analytics help monitor inventory levels, ensuring timely restocking and minimizing holding costs. ERP systems integrate various functions, such as procurement, sales, and inventory management, providing a comprehensive view of the supply chain. This integration allows companies to monitor inventory levels, track stock movements, and identify potential shortages.
Data analytics can also provide insights into demand patterns, enabling companies to forecast inventory needs accurately. Analyzing historical sales data, seasonal trends, and market fluctuations can help adjust inventory levels accordingly. These technologies contribute to efficient inventory management, reducing costs and maintaining balanced supply chains.
In Conclusion
Transportation, warehousing, and inventory management form the backbone of logistics, ensuring seamless coordination across supply chains. Transportation manages the movement of goods, optimizing delivery routes and shipment consolidation. Warehousing provides storage solutions, balancing supply and demand while minimizing costs. Inventory management focuses on balancing supply and demand, implementing strategies such as JIT to reduce holding costs. Understanding these key functions provides a comprehensive approach to logistics, contributing to efficient operations and sustainable business growth.