Supply Chain Management (SCM) is the lifeblood of the global economy, orchestrating the flow of goods, information, and finances from the initial procurement of raw materials to the delivery of finished products to end consumers. It encompasses a broad range of activities—procurement, manufacturing, distribution, and more—each critical to the efficient and effective operation of businesses across industries. SCM’s strategic role extends far beyond mere logistics or procurement; it is about creating a seamless, integrated process that enhances efficiency, minimizes costs, and maximizes customer satisfaction. In today’s interconnected and highly competitive global market, SCM stands as a pivotal element in maintaining the flow of goods across borders, ensuring that businesses can meet their customers’ demands promptly and efficiently. This article aims to shed light on the intricate world of SCM, demystifying its components, addressing common challenges, and highlighting its undeniable importance in today’s economy.
Understanding the Components of SCM
Procurement and Sourcing
Procurement and sourcing are the cornerstones of effective SCM, involving the strategic selection and acquisition of raw materials and services needed to produce goods or services. This process is not just about finding the lowest cost but also about ensuring quality, reliability, and sustainability from suppliers. Strategic sourcing decisions can significantly impact production efficiency, cost management, and even the overall sustainability of the supply chain.
Production and Manufacturing
The production and manufacturing phase is where raw materials are transformed into finished goods. Effective SCM ensures that this process is carried out efficiently, with minimal waste and maximum productivity. This involves detailed production planning, scheduling, and quality control measures to ensure that products meet the required standards and are produced on time to meet market demand.
Distribution and Logistics
Once goods are produced, they need to be distributed to retailers or directly to consumers. The distribution and logistics component of SCM covers the warehousing, transportation, and delivery of products. Efficient logistics operations are vital to minimize costs, ensure timely delivery, and maintain product quality during transit.
Demand Planning and Customer Service
SCM is not just about the physical movement of goods; it also involves planning and forecasting to align production and inventory levels with market demand. This component ensures that businesses can respond quickly to changes in consumer preferences and market conditions. Furthermore, effective SCM enhances customer service by ensuring product availability, providing accurate delivery information, and efficiently handling returns and exchanges.
The Strategic Importance of SCM in Modern Business
Driving Operational Efficiency
SCM is instrumental in streamlining operations across the supply chain, reducing waste, and improving time management. By optimizing each component of the supply chain, businesses can achieve significant cost savings, enhance productivity, and ultimately increase their bottom line.
Enhancing Customer Satisfaction
At its core, SCM is about delivering the right product, in the right quantity, at the right time, and to the right place. By efficiently managing the supply chain, businesses can ensure customer satisfaction through timely deliveries, high-quality products, and excellent post-purchase support, fostering loyalty and repeat business.
Facilitating Global Expansion
For businesses looking to expand globally, SCM plays a crucial role in navigating the complexities of international trade, including compliance with local regulations, customs clearance, and managing global logistics networks. Effective SCM strategies enable businesses to tap into new markets, source materials from around the world, and compete on a global stage.
Supply Chain Management is an integral part of modern business strategy, driving efficiency, customer satisfaction, and global expansion. Its comprehensive scope, encompassing procurement, production, distribution, and demand planning, ensures that businesses can meet the challenges of today’s dynamic market environment.
How to Optimize Your SCM Strategy
Optimizing your supply chain management (SCM) strategy is crucial for staying competitive in today’s fast-paced market. By leveraging technology, building resilience, and focusing on sustainability and ethics, businesses can create efficient, transparent, and responsible supply chains.
Leveraging Technology for Enhanced SCM
Incorporating advanced technology into your SCM strategy can significantly improve efficiency and transparency across your supply chain. SCM software platforms offer comprehensive tools for inventory management, procurement, logistics, and more, enabling businesses to streamline operations and reduce manual errors. Internet of Things (IoT) devices allow for real-time tracking of goods, providing valuable data that can be used to optimize routes, predict maintenance, and prevent losses. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and blockchain technology can further enhance decision-making and security. AI offers predictive analytics for demand forecasting and inventory optimization, while blockchain provides a secure and transparent way to document transactions, improving trust among stakeholders.
Building Resilient Supply Chains
Creating a resilient supply chain is essential for mitigating risks and ensuring business continuity in the face of disruptions. Diversification of suppliers and flexible sourcing strategies can protect your supply chain from regional disruptions and market volatility. Implementing robust risk management practices, such as regular risk assessments and developing contingency plans, ensures that your business can respond quickly and effectively to unforeseen challenges. Collaboration and communication with suppliers and logistics partners are also key to building a resilient supply chain that can adapt to changes and recover from setbacks.
Sustainability and Ethics in SCM
Sustainability and ethical considerations are becoming increasingly important in SCM. Implementing sustainable practices, such as optimizing transportation routes to reduce carbon emissions, choosing eco-friendly packaging, and minimizing waste, demonstrates corporate responsibility and can lead to cost savings. Ethical sourcing and fair labor practices are also critical components of a responsible supply chain. Businesses should work closely with suppliers to ensure that materials are sourced sustainably and that workers are treated fairly, fostering a positive brand image and customer trust.
Unveiling the Dynamics of Supply Chain Management
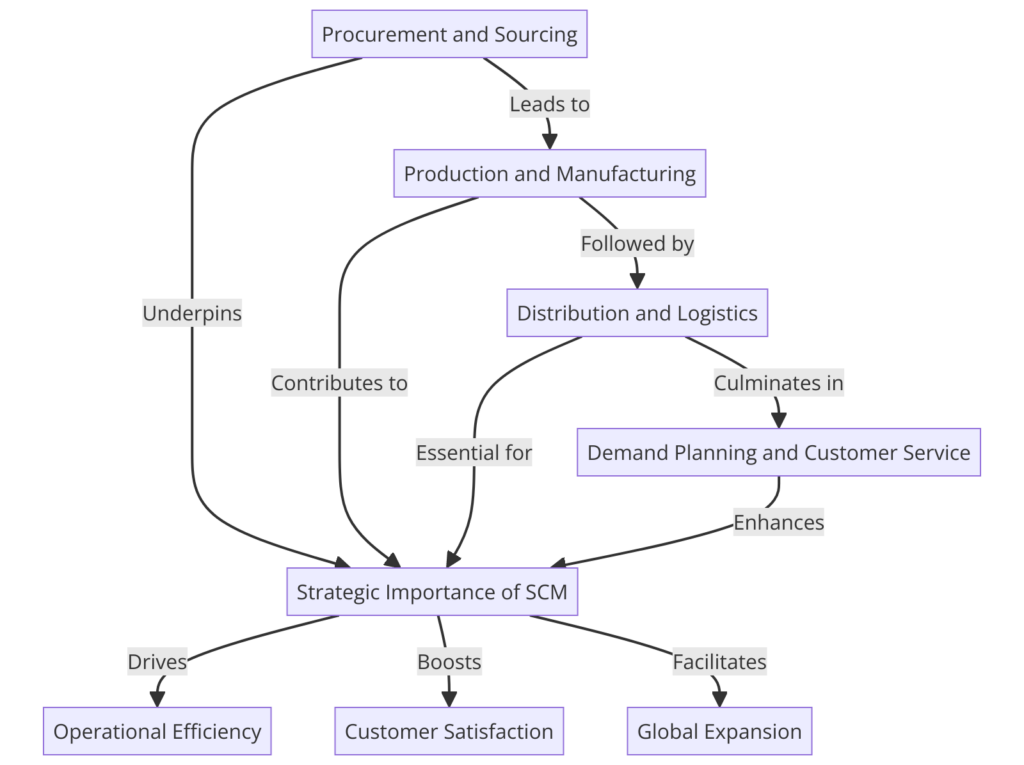
Supply Chain Management (SCM) represents a critical framework within the global economy, orchestrating the flow of goods, information, and finances from inception to consumption. Its significance lies not only in facilitating the movement of goods across borders but also in optimizing this journey to achieve efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and customer satisfaction. Through a strategic integration of procurement, production, distribution, and demand planning, SCM ensures that businesses can effectively meet consumer demands while fostering economic growth and sustainability.
Procurement and Sourcing: The initiation of the supply chain, where strategic decisions regarding the acquisition of raw materials and services lay the foundation for production efficiency and sustainability.
Production and Manufacturing: The transformation phase, where raw materials undergo manufacturing processes to become finished goods, underscored by an emphasis on efficiency and quality control.
Distribution and Logistics: The delivery mechanism, ensuring that finished products reach their final destinations through efficient logistics and transportation strategies.
Demand Planning and Customer Service: The predictive and responsive facet of SCM, where market demand is forecasted and met, ensuring product availability and customer satisfaction.
SCM transcends traditional boundaries, playing a strategic role in modern business operations. It navigates the complexities of global trade, technological advancements, and the imperative for sustainable practices, making it indispensable in today’s interconnected market landscape.
By understanding and optimizing these components, businesses can not only streamline their operations but also enhance their competitive edge, adapt to market changes, and contribute to a sustainable economic future.
5 Key Trends Shaping the Future of SCM
1. Digital Transformation
The digital transformation of SCM is revolutionizing the way businesses manage their supply chains. Automation, powered by AI and machine learning, is streamlining processes from procurement to delivery. Data analytics provide insights that drive smarter, more strategic decision-making, enhancing efficiency and competitiveness.
2. Sustainability and Circular Economy
The shift towards sustainability and a circular economy is reshaping SCM. Businesses are rethinking their supply chain models to minimize environmental impact, focusing on recycling, reusing, and reducing waste. This not only addresses environmental concerns but also meets the growing consumer demand for sustainable products and practices.
3. Customer-Centric Supply Chains
The move towards customer-centric supply chains emphasizes personalization and responsiveness to customer needs. This trend involves tailoring logistics processes and services to enhance customer satisfaction, such as offering flexible delivery options and transparent tracking. Engaging customers through personalized supply chain practices can lead to increased loyalty and competitive advantage.
4. Global Supply Chain Visibility
Achieving end-to-end visibility across the supply chain is crucial for effective management and decision-making. Technology plays a key role in this trend, with IoT devices and cloud-based platforms providing real-time data on inventory levels, shipment statuses, and potential disruptions. Enhanced visibility enables businesses to respond swiftly to challenges, ensuring the smooth flow of goods and services.
5. Agility and Flexibility
In today’s dynamic market, agility and flexibility are essential for SCM. Supply chains must be able to rapidly adapt to changes, such as fluctuating demand, market disruptions, or new regulatory requirements. Emphasizing agility in SCM allows businesses to seize opportunities, mitigate risks, and maintain competitive edge.
The Evolution of SCM in the Digital Age
The digital age has ushered in a transformative era for Supply Chain Management (SCM), marked by the integration of groundbreaking technologies that are reshaping the landscape of global commerce. As SCM evolves, it stands at the intersection of innovation and efficiency, navigating through challenges and seizing new opportunities.
The Integration of Advanced Technologies in SCM
The incorporation of Artificial Intelligence (AI), machine learning, and blockchain technology has revolutionized SCM, offering unprecedented capabilities for optimizing operations. AI and machine learning algorithms can predict market demand, automate inventory management, and enhance decision-making processes, leading to significant reductions in waste and improvements in efficiency. Blockchain technology, on the other hand, introduces a new level of transparency and security to the supply chain, enabling real-time tracking of goods and ensuring the integrity of transactions. These advanced technologies not only streamline operations but also open up new avenues for creating value within the supply chain.
Navigating Challenges and Seizing Opportunities
While the digital transformation of SCM offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges for businesses. The adoption of new technologies requires significant investment in infrastructure and skills development, and there can be resistance to change within organizations. Additionally, the complexity of integrating digital solutions across a global supply chain can be daunting. However, these challenges are outweighed by the opportunities that digital SCM presents for businesses to gain a competitive edge. Companies that successfully navigate these hurdles can achieve greater operational flexibility, reduce costs, and better meet customer demands, positioning themselves as leaders in the digital economy.
Some FAQs Answered on The Relevant Topic
What distinguishes SCM from logistics?
While logistics focuses primarily on the transportation and storage of goods, SCM encompasses a broader spectrum of activities, including procurement, production planning, inventory management, and distribution. SCM seeks to optimize the entire supply chain from end to end, whereas logistics is one component of that chain.
How does SCM contribute to a company’s competitive advantage?
Effective SCM can significantly enhance a company’s competitive advantage by improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, increasing speed to market, and ensuring customer satisfaction. By closely aligning the supply chain with business strategy, companies can respond more swiftly to market changes and customer needs.
What are the essential skills needed for effective SCM?
Key skills for SCM professionals include analytical thinking, proficiency in technology, understanding of global supply chain dynamics, strategic planning, and effective communication. Familiarity with SCM software and emerging technologies such as AI and blockchain is also increasingly important.
How do small businesses benefit from implementing SCM practices?
Small businesses can gain from SCM practices by improving efficiency, reducing operational costs, and enhancing customer satisfaction. Even basic SCM strategies can help small businesses better forecast demand, manage inventory more effectively, and develop stronger relationships with suppliers, enabling them to compete more effectively in the market.
In Conclusion
The evolution of Supply Chain Management in the digital age represents a pivotal shift towards greater efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness. Through the strategic integration of advanced technologies like AI, machine learning, and blockchain, SCM is being transformed into a more dynamic, transparent, and efficient process. Despite the challenges associated with adopting these technologies, the opportunities they present for business innovation and competitive advantage are significant. As we reflect on the transformative impact of emerging trends and technologies on SCM, it becomes clear that the continuous adaptation and innovation of supply chain strategies are crucial for businesses aiming to thrive in today’s interconnected and rapidly evolving global economy. Embracing the digital transformation of SCM is not just an operational necessity but a strategic imperative for driving sustainable growth and maintaining global competitiveness.