As the logistics industry evolves, the emphasis on sustainable practices has grown significantly. The demand for greener logistics solutions is driven by both regulatory pressures and the increasing consumer demand for environmentally friendly operations. Embracing sustainable logistics not only helps reduce environmental impact but also enhances efficiency and brand reputation. This article explores ten key sustainable practices that can transform logistics operations, reduce carbon footprints, and promote a greener future.
Logistics plays a pivotal role in the global economy, but it is also a major contributor to carbon emissions and environmental degradation. As companies and consumers become more environmentally conscious, the need for sustainable logistics practices has never been more urgent. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of practical, actionable steps that logistics companies can take to reduce their environmental impact while maintaining efficiency and profitability.
1. Electrification of Fleet
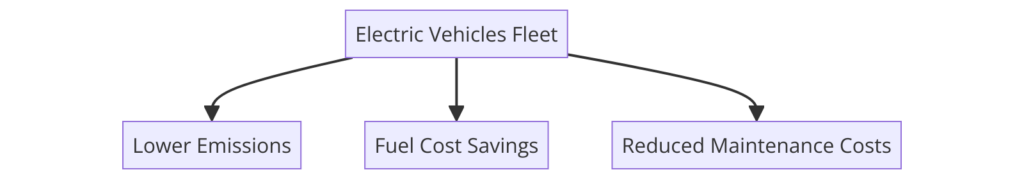
One of the most impactful changes in green logistics is the transition to electric vehicles (EVs). Electric trucks and delivery vans significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to their diesel counterparts. Companies like DHL are leading the way, aiming to have 60% of their last-mile fleet powered by electricity by 2030 . The adoption of e-cargo bikes for urban deliveries is also on the rise, further reducing emissions and alleviating traffic congestion.
Electrifying the fleet involves initial investment in vehicles and charging infrastructure, but the long-term benefits include lower operating costs and compliance with emerging emission regulations. Businesses can leverage government incentives and subsidies to offset the upfront costs associated with transitioning to electric vehicles. Additionally, electric vehicles require less maintenance than traditional combustion engines, leading to further cost savings over time.
2. Optimizing Route Planning
Efficient route planning is essential for minimizing fuel consumption and reducing emissions. Advanced route optimization software uses real-time data to find the most efficient routes, considering factors like traffic conditions, delivery windows, and vehicle capacity. This technology helps eliminate unnecessary mileage and ensures timely deliveries .
AI-driven route planning not only enhances operational efficiency but also improves customer satisfaction by providing accurate delivery times. Companies can significantly cut down on fuel costs and reduce their carbon footprint through optimized logistics operations. Furthermore, integrating AI with GPS and telematics systems allows for dynamic rerouting in response to real-time traffic updates, weather conditions, and other unforeseen disruptions.
3. Sustainable Packaging Solutions
Excessive packaging contributes to waste and environmental degradation. Green logistics emphasizes the use of sustainable packaging materials such as recycled cardboard, biodegradable plastics, and innovative materials like mushroom-based and seaweed-based packaging . These materials reduce the environmental impact and cater to the growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
Implementing sustainable packaging solutions involves assessing the entire packaging lifecycle, from sourcing to disposal. Encouraging customers to return packaging for recycling or reuse can further enhance sustainability efforts and reduce waste. Companies can also explore minimalist packaging designs that use less material without compromising product protection, thereby reducing both costs and environmental impact.
4. Implementing Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics involves the efficient management of product returns, recycling, and disposal. This practice supports a circular economy by extending the lifecycle of products through recycling, refurbishing, and reselling. Companies like H&M have successfully implemented reverse logistics programs to manage garment returns and recycling .
Adopting reverse logistics requires robust systems for tracking and managing returned goods. Integrating IoT and RFID technologies can streamline this process, ensuring efficient handling and reducing the environmental impact of returns. Effective reverse logistics not only contributes to sustainability but also enhances customer satisfaction by providing convenient return options and ensuring quick processing of returned items.
5. Leveraging Renewable Energy
Using renewable energy sources is a cornerstone of sustainable logistics. Warehouses and distribution centers can be equipped with solar panels and wind turbines to generate clean energy. This not only reduces carbon emissions but also lowers energy costs .
Investing in renewable energy solutions aligns with global sustainability goals and enhances the corporate image. Government grants and incentives are often available to support the transition to renewable energy, making it a financially viable option for many businesses. Additionally, energy storage systems such as batteries can help manage energy use more efficiently by storing excess renewable energy for use during peak demand periods.
6. Collaboration with Green Suppliers
Sustainable logistics extends beyond internal operations to the entire supply chain. Collaborating with suppliers who prioritize sustainability ensures that eco-friendly practices are maintained throughout the logistics network. This includes sourcing materials from sustainable sources and working with suppliers who use green technologies .
Engaging in regular audits and assessments of supplier practices helps maintain high standards of sustainability. Transparent communication about sustainability goals and expectations fosters strong partnerships and mutual commitment to environmental stewardship. By building a network of green suppliers, companies can enhance their overall sustainability and contribute to broader environmental initiatives.
7. AI and Big Data Analytics
AI and big data analytics play a crucial role in optimizing logistics operations for sustainability. Predictive analytics can forecast demand and optimize inventory levels, reducing waste and improving efficiency. AI can also identify areas of energy wastage within warehouses, suggesting improvements to reduce consumption .
Implementing AI-driven solutions enables real-time monitoring and decision-making, enhancing the agility and responsiveness of logistics operations. This technology ensures that resources are used efficiently, minimizing the environmental impact. Data analytics can also help identify patterns and trends, providing insights that can drive continuous improvement in sustainability efforts.
8. Green Warehousing Practices
Green warehousing practices involve adopting energy-efficient technologies and sustainable building designs. This includes using LED lighting, automated systems powered by renewable energy, and climate control systems that minimize energy use. Green warehouses reduce operational costs and contribute to overall sustainability goals.
Retrofitting existing warehouses with energy-efficient technologies can provide significant environmental benefits. Additionally, constructing new facilities with sustainability in mind ensures long-term energy savings and reduced carbon footprints. Green building certifications such as LEED can provide guidelines and standards for achieving high levels of sustainability in warehouse design and operation.
9. Reducing Failed Deliveries
Failed deliveries increase transport emissions and operational costs. Implementing solutions like On-Demand Delivery (ODD) allows customers to choose delivery times and locations that suit their schedules, reducing the likelihood of failed attempts. This not only enhances customer satisfaction but also minimizes unnecessary emissions.
Efficient delivery scheduling and real-time communication with customers are key to reducing failed deliveries. Technologies that provide real-time updates and allow for flexible delivery options can significantly improve delivery success rates. By reducing the number of failed deliveries, companies can optimize their logistics operations and minimize their environmental impact.
10. Promoting a Circular Economy
Embracing circular economy principles is essential for sustainable logistics. This involves designing products and processes that prioritize reuse, repair, and recycling. Companies can implement take-back programs and offer incentives for customers to return products at the end of their lifecycle .
A circular economy reduces the reliance on raw materials and minimizes waste, contributing to environmental sustainability. Educating customers and stakeholders about the benefits of a circular economy fosters a culture of sustainability and supports long-term environmental goals. By promoting practices that extend the life of products and materials, companies can achieve significant environmental and economic benefits.
In conclusion, implementing sustainable practices in logistics is not only crucial for environmental protection but also for achieving operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. By adopting practices such as electrifying fleets, optimizing routes, using sustainable packaging, implementing reverse logistics, leveraging renewable energy, collaborating with green suppliers, utilizing AI and big data, adopting green warehousing practices, reducing failed deliveries, and promoting a circular economy, businesses can significantly reduce their environmental impact. As the logistics industry continues to evolve, staying committed to sustainability will ensure long-term success and resilience in a rapidly changing world.